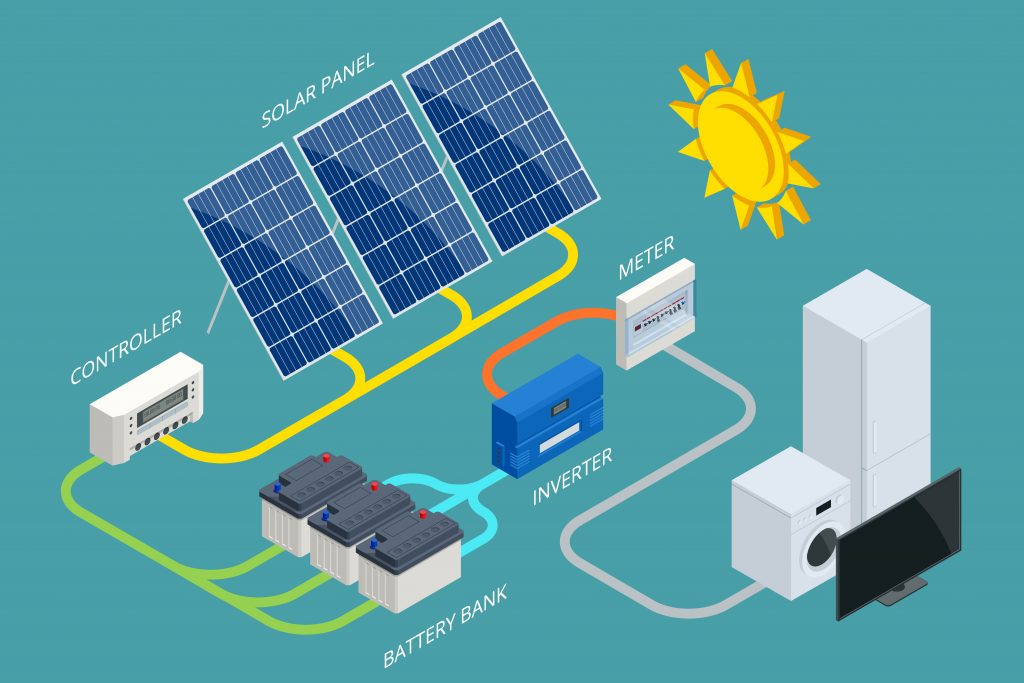
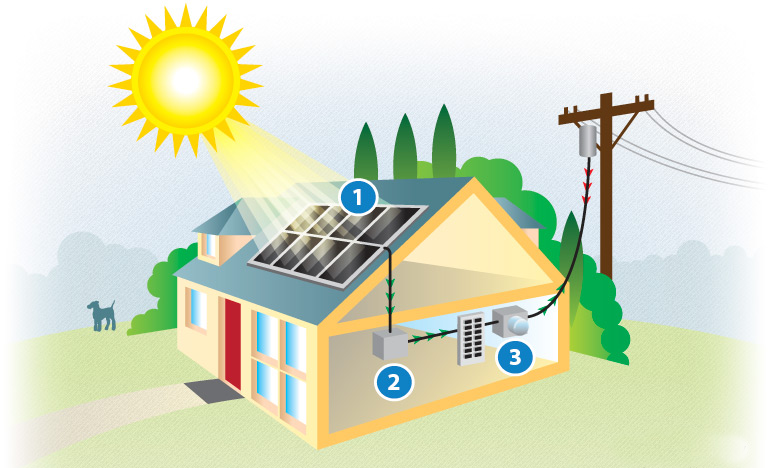
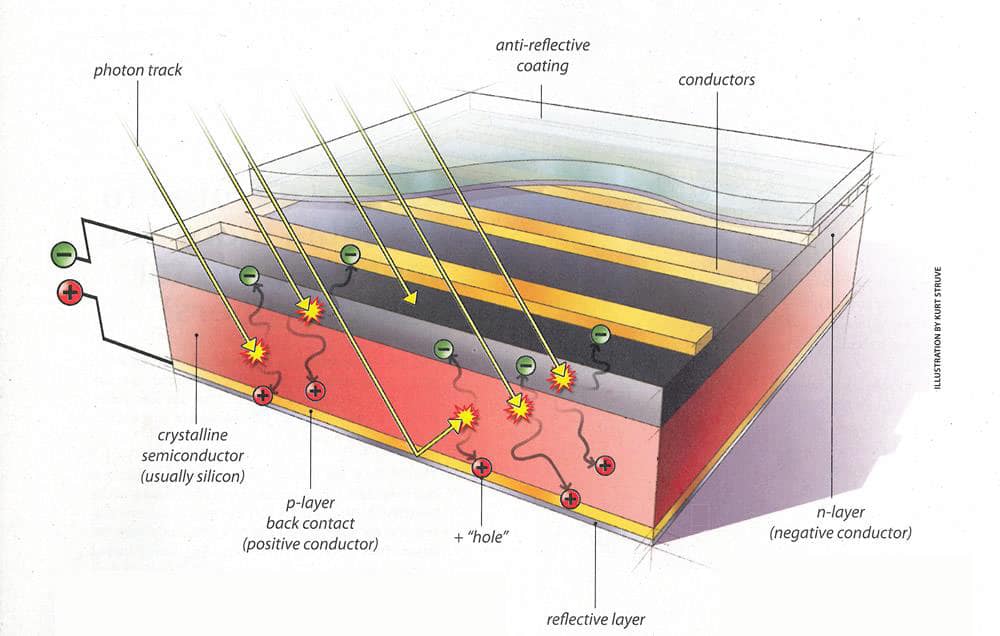
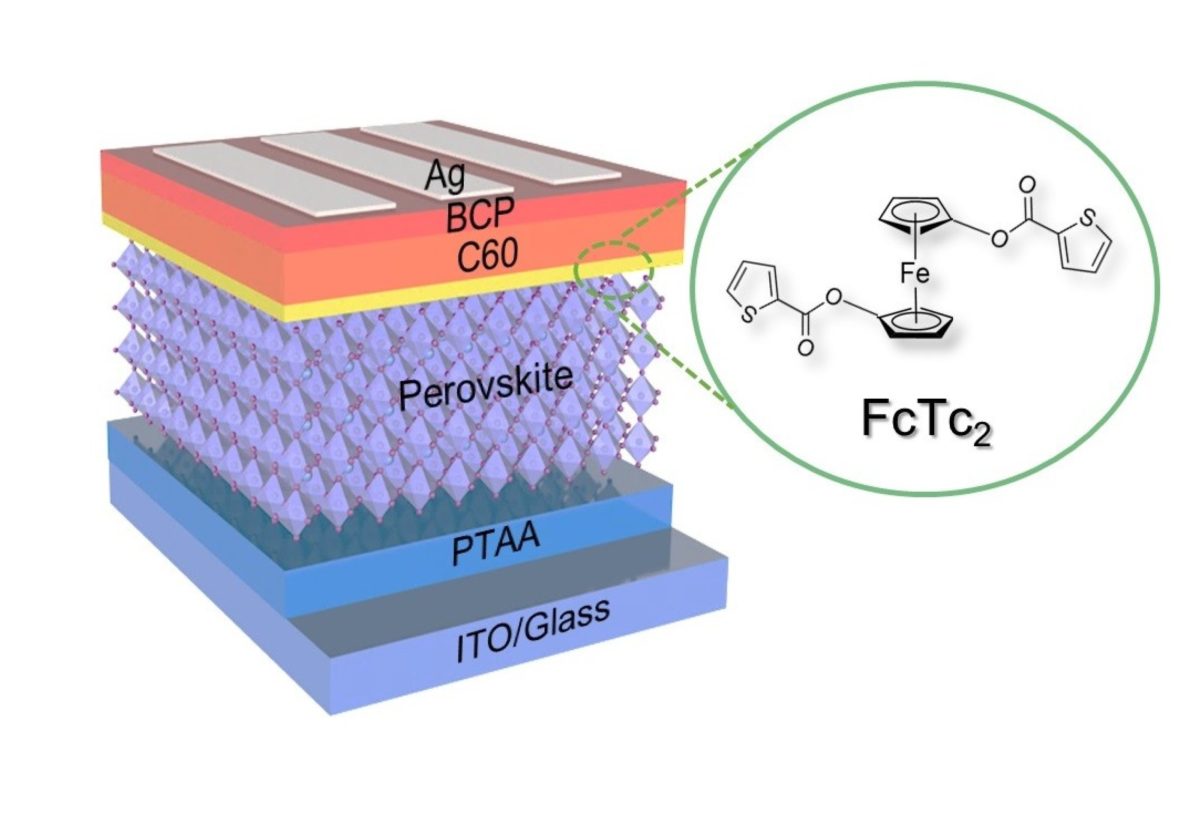
SOLAR ENERGY
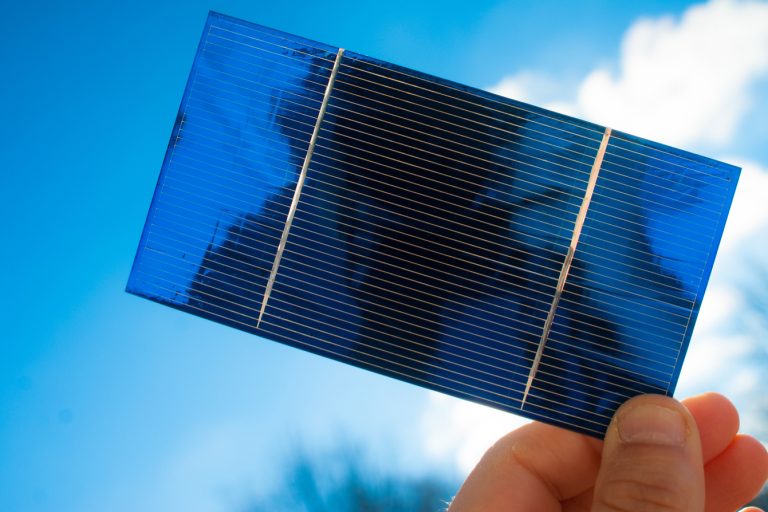
Every day, Indians are making the choice to power their lives with solar energy either through installing it on their rooftops or for commercial use . Over the next few years, millions more will take advantage .
MTAK is connecting the dots for you—demonstrating how solar energy investments accrue over years to benefit individuals, communities, and the nation,and the importance of skilled manpower.




A small river named Duden flows by their place and supplies it with the necessary regelialia.
It is a paradisematic country, in which
MTAK Pedagogy
Identify and Engage Strong Partners
The challenges any evolving company face — no organization can tackle them alone. MTAK convenes and engages strong partners from across fields and industries who can break down complicated issues, innovate, and share solutions that work.
Approach in Action
The Team collaborates with key partners like Hospitals, Energy Parks, Schools, and other civic bodies to enhance Technical Infrastructure.
New Energy & Health care Alliance for Country to Create Exponential Growth in Renewable Energy, Healthcare & Education
“We are Team Malwa”